Our Specialties
Thyroid Nutritionists Near Me
90% of Zaya patients pay $0 for one-on-one nutrition counseling with a registered dietitian.
Find A Thyroid Nutritionist Near MeBrowse our directory of thyroid nutritionists — and book your visit online using your insurance.
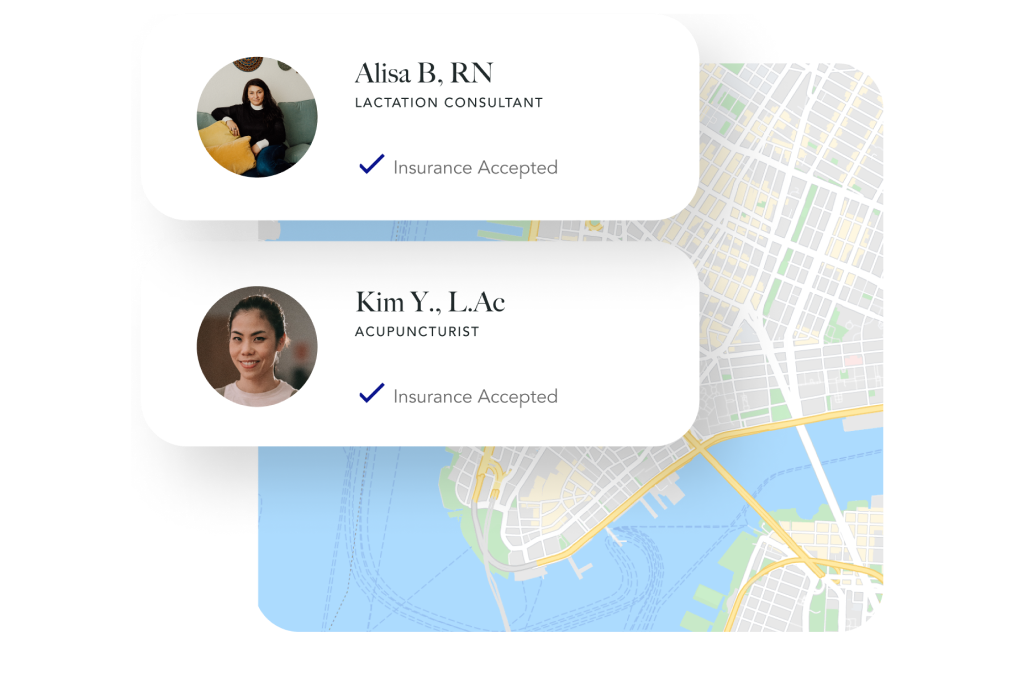
Find the right care for you.

Pay with your insurance.
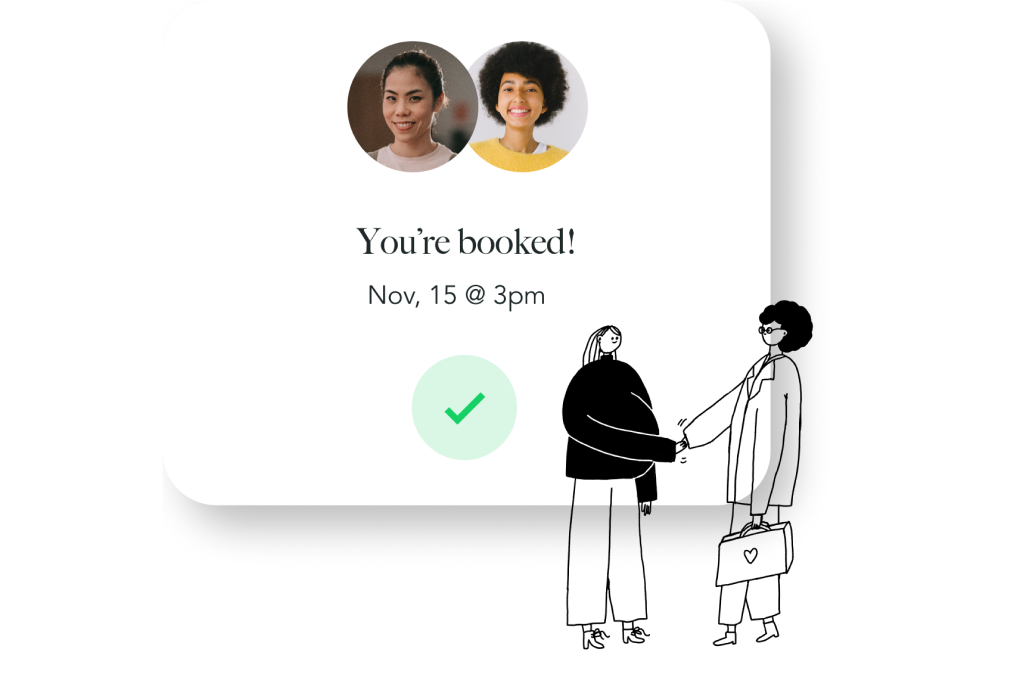
Book your visit online.
Get a provider who gets you.
Our providers are nutrition experts and take the time to get to know you and your needs.
Real talk from real patients.
Have questions? We’ve got answers.
For more information about how Zaya works, check out our frequently asked questions.
View FAQsMore about thyroid disorders & our thyroid dietitians
What does the thyroid do?
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. Its primary function is to produce and release hormones that regulate various metabolic processes in the body.
These hormones, known as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), play a crucial role in controlling the body’s energy production and consumption.
The thyroid gland helps regulate metabolism, which affects how the body uses energy from food. It influences processes such as heart rate, body temperature, digestion, and the rate at which cells convert nutrients into energy.
Additionally, thyroid hormones are involved in the development and functioning of the brain, muscles, and other organs.
Overall, the thyroid gland acts as the body’s metabolic regulator, ensuring that essential functions are carried out at the appropriate rate. By producing and releasing thyroid hormones, it helps maintain a balanced and efficient metabolism throughout the body.
What are thyroid disorders?
Thyroid disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the function and structure of the thyroid gland. Here are some common thyroid disorders:
- Hypothyroidism. A condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland that doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones, resulting in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
- Hyperthyroidism. An overactive thyroid gland that produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and irritability.
- Thyroid nodules. Abnormal growths or lumps in the thyroid gland that can be benign or cancerous.
- Thyroiditis. Inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by viral or autoimmune factors and may result in temporary hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
- Graves’ disease. An autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excess thyroid hormones and leading to symptoms such as bulging eyes, anxiety, and heat sensitivity.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Another autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing chronic inflammation and eventually leading to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid cancer. The development of cancerous cells in the thyroid gland, which can be of different types and may require surgical intervention and other treatments.
What causes thyroid disorders?
Thyroid disorders can arise from various factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. Here are some common causes of thyroid disorders:
- Autoimmune conditions. Conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, can lead to inflammation and alterations in thyroid hormone production.
- Iodine deficiency. Inadequate intake of iodine, an essential mineral required for producing thyroid hormones, can contribute to thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism.
- Genetics. Certain genetic factors can predispose individuals to thyroid disorders, including a family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases or certain genetic mutations associated with thyroid function.
- Radiation exposure. Radiation exposure from medical treatments or environmental sources can increase the risk of developing thyroid disorders, including thyroid cancer.
- Medications and treatments. Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can affect thyroid function. Additionally, treatments like radiation therapy or surgical removal of the thyroid gland can impact thyroid hormone production.
- Pregnancy and hormonal changes. Pregnancy and postpartum hormonal changes can sometimes trigger or exacerbate thyroid disorders, particularly postpartum thyroiditis.
What are the symptoms of thyroid disorders?
Thyroid disorders affect a significant number of individuals, with many being unaware of their condition. An estimated 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease, and up to 60% of those affected may not realize they have a thyroid disorder.
The symptoms of thyroid disorders can vary depending on whether the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Here are some common symptoms associated with thyroid disorders.
Hyperthyroidism:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Nervousness, irritability, or anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Fatigue or muscle weakness
- Changes in menstrual patterns
Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair
- Constipation
- Depression or mood swings
- Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
- Joint pain or stiffness
What are the risks of thyroid disorders?
Untreated thyroid disorders can lead to various risks and complications impacting a person’s health and well-being. It is important to address these conditions to prevent potential adverse effects.
Here are some risks and complications associated with untreated thyroid disorders:
- Worsening symptoms. Untreated hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can cause symptoms to persist or worsen over time, decreasing quality of life.
- Cardiovascular issues. Thyroid disorders can increase the risk of heart-related problems, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and an irregular heartbeat.
- Mental health concerns. Untreated thyroid disorders may contribute to mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and cognitive difficulties.
- Infertility and pregnancy complications. Thyroid disorders can affect fertility and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and developmental issues in the baby.
- Metabolic imbalances. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. Untreated thyroid disorders can disrupt this balance, potentially leading to weight changes, difficulty managing weight, and problems with cholesterol levels.
- Goiter or thyroid nodules. In some cases, untreated thyroid disorders can lead to the development of an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) or abnormal growths or nodules within the thyroid gland.
When to see a thyroid dietitian
When managing thyroid conditions, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, working with a thyroid dietitian can be beneficial in optimizing overall health and supporting thyroid function.
A thyroid dietitian specializes in understanding the impact of nutrition on thyroid health and can provide personalized guidance to individuals with thyroid disorders. You should consider working with a thyroid nutritionist if you:
- Are newly diagnosed with a thyroid disorder. A thyroid dietitian can help you navigate the dietary changes that may be necessary following a diagnosis, ensuring that you are meeting your nutritional needs and supporting thyroid function.
- Experience weight changes or difficulties managing weight. Weight fluctuations are common with thyroid disorders. A thyroid nutritionist can develop a tailored nutrition plan to support healthy weight management and address any underlying metabolic imbalances.
- Have persistent fatigue or low energy levels. Fatigue is a common symptom of thyroid disorders. A thyroid dietitian can identify dietary factors that may contribute to fatigue and recommend energy-boosting foods to incorporate into your diet.
- Have digestive issues or food sensitivities. Thyroid disorders can sometimes coincide with digestive problems or food sensitivities. A thyroid nutritionist can help identify trigger foods, design a gut-friendly diet plan, and ensure proper nutrient absorption.
- Are planning or undergoing thyroid treatment. Whether you’re considering radioactive iodine therapy or undergoing thyroid surgery, a thyroid dietitian can guide you on dietary adjustments that may be necessary before, during, and after treatment to support healing and optimize outcomes.
- Have concerns about nutrient deficiencies. Certain nutrients, such as iodine, selenium, and zinc are essential for proper thyroid function. A thyroid nutritionist can assess your nutrient status and recommend appropriate dietary modifications.
How Zaya Care’s thyroid nutritionists can help
Working with a dietitian specializing in thyroid disorders can provide valuable support and guidance in managing your condition. In the first appointment, you can expect the nutritionist to conduct a thorough assessment of your medical history, current symptoms, and dietary habits.
They will work with you to develop a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your specific thyroid needs, taking into account nutrient requirements, potential deficiencies, and any food sensitivities or allergies you may have.
During follow-up appointments, the nutritionist will monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your nutrition plan based on your response and evolving health goals. They will provide ongoing support, education, and guidance to help you make sustainable dietary changes.
Additionally, they may offer meal planning tips, recommend specific foods to include or avoid, and provide strategies for managing common symptoms associated with thyroid disorders, such as fatigue or weight changes.
Benefits of working with a Zaya Care thyroid dietitian
Zaya Care’s thyroid dietitians provide personalized and evidence-based nutrition guidance to improve your thyroid health. Our experts are well-versed in managing thyroid disorders through diet and nutrition, keeping up with the latest research and recommendations.
When you work with our team, your dietitian will consider your medical history, dietary preferences, and lifestyle factors to create a customized plan. They will incorporate foods that can alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being.
We understand the emotional aspects of food and eating, and our nutritionists provide a supportive environment to address any issues related to your relationship with food. They will guide you in developing a healthier approach to eating and overcoming emotional eating.
Throughout your health journey, your dietitian will offer ongoing support, motivation, and accountability. They will assist you with meal planning, navigating social situations, and making informed choices that optimize your thyroid health and overall wellness.
Working with a Zaya Care nutritionist specializing in thyroid disorders empowers you to take control of your nutrition and make positive changes for your health. Our team is committed to helping you achieve your goals and enhance your quality of life.




